The stages of psoriasis are defined over the time period in which the disease has characteristic features. Many people with psoriasis mistakenly refer to this stage as a serious or mild form of illness, but in the medical record, the term is used with a completely different meaning.
What are the stages of psoriasis?
Psoriasis is considered a recurrent skin condition, in which it is inherited. According to statistics of dermatologists, at least 2% of the world's population suffer from this disease, which means that the problem is very urgent. In psoriasis, 2 conditions are clearly distinguished:
- Recurrence.This term refers to skin deterioration. When it comes back, the patient experiences itching, pain, burning, a severe skin rash, itching, discomfort. The victim's condition was exacerbated by insomnia, psychosis and anxiety.
- Removed.This term is used to mean improving the appearance of the skin. The condition relieved, the skin returned to its normal color, the redness, and the psoriasis skin were also reduced.
The stages of psoriasis partially overlap with the description of remission and relapse, so many dermatologists use these words interchangeably. In clinical practice, the 3 stages of psoriasis are described:
- process stage
- ;
- is fixed; regression phase
- .
Consider that we are talking about a cyclical process, sequential stages that flow together and form a continuous process of disease.
Truth!Progressive phase is considered to be the most difficult to feel.
What is the progression of psoriasis?
The progression phase is triggered by a number of triggers, such as cold or stressful seasons. In some cases, even an experienced dermatologist cannot clearly identify the cause of the disease. During the progression phase the following will happen:
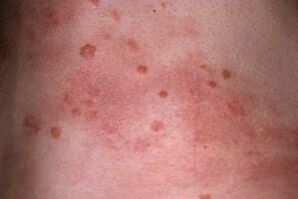
- Psoriasis nodules rapidly grow, affect the skin, bind together in patches, flake and itch. Plaque is a spot of arbitrary shape, usually round or oval, sometimes with irregular edges.
- papules, which are individual nodules of a psoriatic rash, are bumps on the skin. The edges of the papule do not come off, and the center does not come off. When a large number of dead scabs accumulate, plaques begin to emerge on the skin's surface. Puffiness makes them even more bulging and irregular.
- This pathological stage is characterized by an isotropic reaction, including a worsening rash in the case of skin lesions, abrasions, injections, cuts, small wounds. This phenomenon is named Köbner.
A slow response characterizes the advanced stage of psoriasis. In some cases, skin rashes appear about 9 days after exposure to an irritant (such as a food allergen). Usually, a psoriatic rash appears within 24 hours of exposure to the adverse factors.
Interesting!95% of people with psoriasis have some intolerant foods that can cause relapses. To avoid an exacerbation, keep a diary of your food intake and reactions to different foods.
Static and diving stages
The sedentary phase is the stage in the psoriasis where the victim's condition is relatively stable. In the static phase:
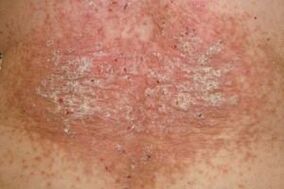
- Scaly plaques with smooth borders. The entire surface of the plaque is covered with a thick, flaky scale. Moderate itching and discomfort. Around the papules do not have bright red inflammatory rim.
- For skin microflora, the Koebner phenomenon was not observed, ie scratching or cutting the healed skin no longer turned into a scaly plaque.
The recessive or recessive stage is characterized by large lesions in psoriasis. First, a atrophic pseudosphere can be seen around the papules, then the patient notices a rapid cessation of exfoliation, with the formation of hyperpigmentation plaques in place.
Severity of disease
An additional diagnostic criterion is the assessment of the area of a psoriatic lesion. The term "severity" is used to describe it. Dermatologists distinguish 3 severity of skin diseases:
- Easy.Psoriasis plaques occupy 1 to 3% of the total body area. The small size of the affected areas doesn't mean the patient is doing well. With psoriasis in the head or face, even a few patches are enough to cause discomfort and pain for the patient.
- Medium.The volume of psoriasis eruptions accounts for 3 to 10% of the total body area. In this case, the back, chest and outer surfaces of the joints, scalp, palms, and feet are affected. This prevalence resulted in severe intoxication and severe pain. The patient may lose all or part of the ability to work, and the mental and nervous system of the nervous system deteriorate.
- Heavy.The disease covers more than 10-15% of the skin's surface. According to preliminary estimates, if psoriasis occupies more than a quarter of the total body area, the possibility of liver and kidney failure increases many times. Decompensated damage to internal organs can cause fatal psoriasis.
To fully assess the severity of psoriasis, a special scale called PASI is used. Scale takes into account:
- percentage of healthy and diseased skin;
- pathological stage;
- patient's response to drug therapy;
- individual tolerance to psoriasis (mental states, complications from the nervous and mental system);
- objective data of laboratory kinetic assays (eg volume of uric acid in blood test).
Diagnosis considers all the symptoms affecting the condition of a person with psoriasis. Intensity is reflected in the medical record:
- the itchy process of the skin
- ;
- redness;
- puffiness;
- increased blood pressure;
- thick skin;
- exfoliates;
- blood flow;
- swelling; infection
- ; pain syndrome
- .
According to the PASI scale, the skin lesion volume is described by numbers, from 0 to 72, where 0 is asymptomatic and 72 is the largest possible extent of the disease.
Attention!First of all, it is important for the patient to know and watch for signs of exacerbation. If adverse symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a dermatologist, as psoriasis does not always enter a sedentary phase. A relapse can last for decades.
Treatment of psoriasis is stage-dependent
For each stage of the disease, a set of therapies have been developed, so the first thing a dermatologist does is determine whether the psoriasis is progressing, stabilizing or receding. .
How to handle the progression stage
Every person with psoriasis predicts that remission is about to end with his or her own feelings. If the itching gets worse, the skin looks worse and the psoriasis spreads over the body surface, treatment should be initiated. Therapies for the advanced stage have the following features:
- The patient is involved in the prevention of further deterioration, strict adherence to the diet, restriction of the agents of the pathological process (stress, smoking, alcohol).
- For severe itching, antihistamines can be used, an additional benefit of this class of drugs is the elimination of swelling in the area of the psoriatic skin.
- Dermatologists prescribe a range of topical treatments to heal, soften, and thin the skin. At the discretion of the doctor, creams, ointments or sprays are selected. Soap tar and solid oil compression for positive dynamics. You can also apply a compress or apply cosmetics with Dead Sea mud.
The main task at this stage is to end the exacerbation before the disease turns into a long recurrence. According to the indications, the doctor chooses corticosteroids in the form of an injection or in the form of an ointment.
Attention!A short, intensive course of corticosteroids should be used under the supervision of a dermatologist. You can either inject or apply an antihistamine ointment yourself.
Restorative and static phase therapy
Other dermatologist actions depend on the body's response to the chosen treatment. The following may occur:
- The drug has a positive effect. Within 1 to 2 weeks, the psoriasis moves to a sedentary, receding, and remission phase.
- The drug is not working. If no results have been found after 2-4 weeks since the time of prescribing, this is a reason to change the formulary or the treating doctor.
- Aggravating drug. Such dynamics are also possible, especially if the dosage or frequency of taking the drug is insufficient. The disease recurs slowly, the psoriatic plaques cover a large area of the body, the patient needs to be hospitalized.
In a medical setting, more powerful therapies are used, such as hardware dialysis. With a favorable response, psoriasis enters a sedentary phase, which can last from a few days to several months.
Interesting!More than 80% of patients perceive the seasonal nature of exacerbations. This makes the disease predictable and allows you to prepare for the onset of a relapse.
The list of drugs for the discontinuation and regression phase is exactly the same, but with less dosage and frequency of administration compared to the advanced stage.
in remission of 10-15 years
An capable dermatologist sets out the following task - choosing such drugs and physiotherapeutic agents for the longest lasting improvement in psoriasis. At the same time, patients themselves need to try their best to speed up the treatment process, avoid pathogens and use drugs responsibly. If the alliance between the patient and the doctor has developed successfully, the time of remission is unlimited. Stable health can last for 15 years or more.

























